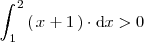Propiedades de la integral definida
De Wikillerato
(Diferencias entre revisiones)
(→Ejemplo 2) |
|||
| (7 ediciones intermedias no se muestran.) | |||
| Línea 100: | Línea 100: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \ge |
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{g} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 117: | Línea 117: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x \ge 0 |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 133: | Línea 133: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | 0 \ge \int_a^ | + | 0 \ge \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 154: | Línea 154: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x > |
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{g} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 171: | Línea 171: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \int_a^ | + | \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x > 0 |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 187: | Línea 187: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | 0 > \int_a^ | + | 0 > \int_a^b \mathrm{f} \left( \, x \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 213: | Línea 213: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \int_1^ | + | \int_1^-1 5 \cdot \left( \, x + 1 \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x = |
| - | + | 15 \cdot \int_1^- \left( \, x + 1 \, \right) \cdot \mathrm{d}x | |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 252: | Línea 252: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
x > x^2, \, \forall x \in \left( \, 0, \, 1 \, \right) | x > x^2, \, \forall x \in \left( \, 0, \, 1 \, \right) | ||
| - | </math> | + | </math>, |
se cumple que | se cumple que | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| Línea 269: | Línea 269: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
x + 1 > 0, \, \forall x \in \left( \, 1, \, 2 \, \right) | x + 1 > 0, \, \forall x \in \left( \, 1, \, 2 \, \right) | ||
| - | </math> | + | </math>, |
se cumple que | se cumple que | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
Revisión actual
Tabla de contenidos |
Propiedades
La integral de la suma de dos funciones es igual a la suma de las integrales de dichas funciones:
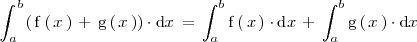
La integral del producto de un número realpor una función es igual al producto de
por la integral de dicha función:
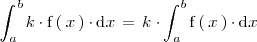
En una integral definida el limite superior de integración puede ser menor que el limite inferior de integración y
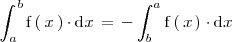
Si hacemos
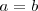 en la igualdad anterior se tiene que
en la igualdad anterior se tiene que
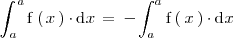
como el único número que coincide con su opuesto es el cero, llegamos a la conclusión de que
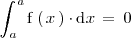
para cualquier número real
 .
.
Dados tres números reales cualesquiera,
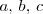 se tiene que:
se tiene que:
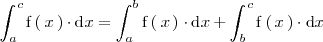
Si en el intervalo
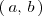 la función
la función
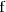 es mayor o igual que la función
es mayor o igual que la función
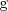 entonces
entonces
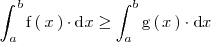
En particular, si
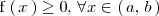 ,
entonces
,
entonces
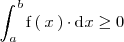
Analogamente, si
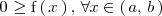 ,
entonces
,
entonces
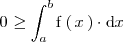
Si en el intervalo
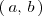 la función
la función
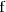 es mayor que la función
es mayor que la función
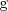 entonces
entonces
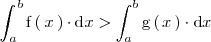
En particular, si
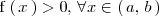 ,
entonces
,
entonces
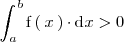
Analogamente, si
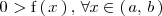 ,
entonces
,
entonces
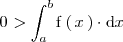
Ejemplo 1
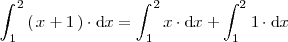
Ejemplo 2
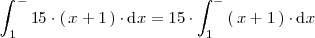
Ejemplo 3
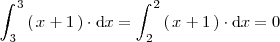
Ejemplo 4
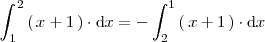
Ejemplo 5
Como
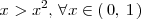 ,
se cumple que
,
se cumple que
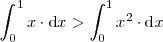
Ejemplo 6
Como
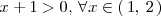 ,
se cumple que
,
se cumple que