Matriz inversa
De Wikillerato
m (Revertidas las ediciones realizadas por 201.171.171.100 (Talk); a la última edición de Laura.2mdc) |
|||
| Línea 1: | Línea 1: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Línea 5: | Línea 7: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | La | + | La matriz inversa de una matriz cuadrada |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A | + | \mathbf{A} |
</math> | </math> | ||
de orden | de orden | ||
| Línea 15: | Línea 17: | ||
es la matriz, | es la matriz, | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A^{-1} | + | \mathbf{A}^{-1} |
</math> | </math> | ||
, de orden | , de orden | ||
| Línea 27: | Línea 29: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A \cdot A^{-1} = A^{-1} \cdot A = I | + | \mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{A}^{-1} = \mathbf{A}^{-1} \cdot \mathbf{A} = I |
</math> | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 56: | Línea 58: | ||
1. Si existe, | 1. Si existe, | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A^{-1} | + | \mathbf{A}^{-1} |
</math> | </math> | ||
es única. | es única. | ||
| Línea 65: | Línea 67: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | A^{-1} | + | \mathbf{A}^{-1} |
\right) | \right) | ||
| - | ^{-1} = A | + | ^{-1} = \mathbf{A} |
</math> | </math> | ||
| Línea 75: | Línea 77: | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | A \cdot B | + | \mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{B} |
\right) | \right) | ||
| - | ^{-1} = B^{-1} \cdot A^{-1} | + | ^{-1} = \mathbf{B}^{-1} \cdot \mathbf{A}^{-1} |
</math> | </math> | ||
| Línea 84: | Línea 86: | ||
==Cálculo de la matriz inversa== | ==Cálculo de la matriz inversa== | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
Para calcular la matriz inversa de una matriz regular podemos utilizar dos procedimientos: | Para calcular la matriz inversa de una matriz regular podemos utilizar dos procedimientos: | ||
| Línea 99: | Línea 102: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A = | + | \mathbf{A} = |
\left( | \left( | ||
\begin{array}[c]{cc} | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| Línea 118: | Línea 121: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A^{-1} = | + | \mathbf{A}^{-1} = |
\left( | \left( | ||
\begin{array}[c]{cc} | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| - | a & b</math> | + | a & b |
| + | \\ | ||
| + | c & d | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Línea 132: | Línea 140: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | I = A \cdot A^{-1} \Rightarrow | + | I = \mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{A}^{-1} \Rightarrow |
\left( | \left( | ||
\begin{array}[c]{cc} | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| Línea 225: | Línea 233: | ||
La inversa de una matriz regular | La inversa de una matriz regular | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | A | + | \mathbf{A} |
</math> | </math> | ||
se calcular transformando la matriz | se calcular transformando la matriz | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | \, A \, \left| \, I \, \right. | + | \, \mathbf{A} \, \left| \, \mathbf{I} \, \right. |
\right) | \right) | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | mediante operaciones | + | mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz |
| - | elementales por filas en la matriz | + | |
<math> | <math> | ||
\left( | \left( | ||
| - | \, I \, \left| \, A^{-1} \, \right. | + | \, \mathbf{I} \, \left| \, \mathbf{A}^{-1} \, \right. |
\right) | \right) | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| Línea 253: | Línea 260: | ||
1. Intercambiar las filas | 1. Intercambiar las filas | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_i | |
</math> | </math> | ||
y | y | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_j | |
| - | </math> | + | </math>. |
| - | | + | Esta operación la representaremos así |
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | F_i \ | + | F_i \longleftrightarrow F_j |
</math> | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Línea 268: | Línea 280: | ||
2. Multiplicar la fila | 2. Multiplicar la fila | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_i | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | por el | + | por el número |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | s \neq 0 | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | y | + | y sustituir |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_i | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| + | por | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | s \cdot F_i | ||
| + | </math>. | ||
| + | Esta operación la representamos de la | ||
| + | siguiente forma: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | <center> | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | s \cdot F_i \longrightarrow F_i | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | 3. Sumar las filas | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_i | |
</math> | </math> | ||
y | y | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | F_j | |
| - | </math> | + | </math>, |
| - | | + | multiplicadas por sendos números, |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | s | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | + | y | |
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | t | |
| - | </math> | + | </math>, |
| - | + | y sustituir | |
<math> | <math> | ||
F_i | F_i | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| - | | + | por el resultado de esta suma. Lo representamos así: |
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | + | s \cdot F_i + t \cdot F_j \longrightarrow F_i | |
</math> | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| - | + | <br/> | |
| - | + | ||
| + | Notese que el segundo tipo de operación, | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | s \cdot F_i \longrightarrow F_i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | | ||
| + | es un caso particular de esta última que se tiene cuando | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | t = 0 | ||
| + | </math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
==Ejercicios resueltos== | ==Ejercicios resueltos== | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | [http://www.educared.net/universidad/asp_problemas/problemasvisualizar.asp?idAsignatura=1&idProblema=46 Producto e invertibilidad de matrices] | ||
[[Category:Matemáticas]] | [[Category:Matemáticas]] | ||
Revisión de 07:06 3 oct 2010
Tabla de contenidos[ocultar] |
Definición
La matriz inversa de una matriz cuadrada
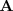 de orden
de orden
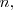 es la matriz,
es la matriz,
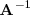 , de orden
, de orden
 que verifica:
que verifica:
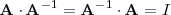
donde
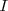 es la matriz identidad de orden
es la matriz identidad de orden
 .
.
Las matrices que tienen inversas se llaman regulares y las que no tienen inversa matrices singulares.
Las propiedades más importantes relativas a la matriz inversa:
1. Si existe,
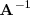 es única.
es única.
2. [Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
3. [Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
Cálculo de la matriz inversa
Para calcular la matriz inversa de una matriz regular podemos utilizar dos procedimientos:
Mediante la definicion
Ejemplo
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
hacemos
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
como
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
Operando:
![\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a + 2c & b + 2d
\\
3a + 7c & 3b + 7d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\Leftrightarrow
\left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a + 2c & = & 1
\\
3a + 7c & = & 0
\\
b + 2d & = & 0
\\
3b + 7d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a + 2c & b + 2d
\\
3a + 7c & 3b + 7d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\Leftrightarrow
\left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a + 2c & = & 1
\\
3a + 7c & = & 0
\\
b + 2d & = & 0
\\
3b + 7d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.](/images/math/math-65ac35f7477a5f157f8f4b5954474b3d.png)
![\Rightarrow \left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a & = & 7
\\
b & = & -2
\\
c & = & -3
\\
d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.
\Rightarrow \left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a & = & 7
\\
b & = & -2
\\
c & = & -3
\\
d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.](/images/math/math-d80915bcc5f5cebafc112b3692daef76.png)
Método de Gauss-Jordan
La inversa de una matriz regular
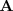 se calcular transformando la matriz
se calcular transformando la matriz
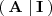 mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz
mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz
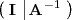
Operaciones elementales por filas en una matriz
Las operaciones elementales por filas en una matriz son las siguientes:
1. Intercambiar las filas
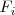 y
y
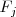 .
Esta operación la representaremos así
.
Esta operación la representaremos así

2. Multiplicar la fila
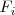 por el número
por el número
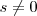 y sustituir
y sustituir
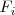 por
por
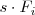 .
Esta operación la representamos de la
siguiente forma:
.
Esta operación la representamos de la
siguiente forma:
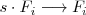
3. Sumar las filas
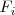 y
y
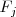 ,
multiplicadas por sendos números,
,
multiplicadas por sendos números,
 y
y
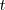 ,
y sustituir
,
y sustituir
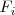 por el resultado de esta suma. Lo representamos así:
por el resultado de esta suma. Lo representamos así:
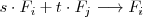
Notese que el segundo tipo de operación,
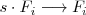 es un caso particular de esta última que se tiene cuando
es un caso particular de esta última que se tiene cuando
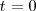 .
.
Ejercicios resueltos
Producto e invertibilidad de matrices



