Matriz inversa
De Wikillerato
(→Calculo de la matriz inversa) |
|||
| Línea 31: | Línea 31: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Las propiedades más importantes relativas a la matriz inversa: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Si existe, | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | A^{-1} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | es única. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | A^{-1} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | ^{-1} = A | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | A \cdot B | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | ^{-1} = B^{-1} \cdot A^{-1} | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Calculo de la matriz inversa= | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Para calcular la matriz inversa de una matriz regular podemos utilizar dos | ||
| + | procedimientos: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Mediante la definicion== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Por ejemplo para hallar la matriz inversa de la matriz | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | A = | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | 1 & 2 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 3 & 7 | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | hacemos | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | A^{-1} = | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | a & b | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | c & d | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | como | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | I = A \cdot A^{-1} \Rightarrow | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | 1 & 2 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 3 & 7 | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | \cdot | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | a & b | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | c & d | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | = | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | 1 & 0 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Operando: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | a + 2c & b + 2d | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 3a + 7c & 3b + 7d | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | = | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{cc} | ||
| + | 1 & 0 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 0 & 1 | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | \Leftrightarrow | ||
| + | \left\{ | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{ccc} | ||
| + | a + 2c & = & 1 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 3a + 7c & = & 0 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | b + 2d & = & 0 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | 3b + 7d & = & 1 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \Rightarrow \left\{ | ||
| + | \begin{array}[c]{ccc} | ||
| + | a & = & 7 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | b & = & -2 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | c & = & -3 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | d & = & 1 | ||
| + | \\ | ||
| + | \end{array} | ||
| + | \right. | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Método de Gauss-Jordan== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | La inversa de una matriz regular | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | A | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | se calcular transformando la matriz | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \, A \, \left| \, I \, \right. | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \left( | ||
| + | \, I \, \left| \, A^{-1} \, \right. | ||
| + | \right) | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Las operaciones elementales por filas en una matriz son las siguientes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Intercambiar las filas | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | y | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | j, | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | que designaremos por | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | F_i \longrightarrow F_j | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Multiplicar la fila | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | por el numero | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | k \neq 0 | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | F_i \tau k \cdot F_i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Multiplicar la fila | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | por el numero | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | k \neq 0 | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | F_i \tau k \cdot F_i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Sumar las filas | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | y | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | j, | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | , multiplicadas por sendos números, y llevar el resultado a la fila | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | o | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | j | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | . Lo designamos por | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | F_i | ||
| + | </math> | ||
| + | o | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | F_j \to k \cdot F_i + t \cdot F_j | ||
Revisión de 12:09 29 nov 2006
La matriz inversa de una matriz cuadrada
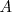 de orden
de orden
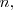 es la matriz
es la matriz
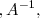 de orden
de orden
 que verifica:
que verifica:
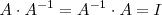
Las matrices que tienen inversas se llaman regulares y las que no tienen inversa matrices singulares.
Las propiedades más importantes relativas a la matriz inversa:
1. Si existe,
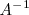 es única.
es única.
2.
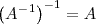
3.
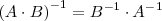
Calculo de la matriz inversa
Para calcular la matriz inversa de una matriz regular podemos utilizar dos procedimientos:
Mediante la definicion
Por ejemplo para hallar la matriz inversa de la matriz
![A =
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 2
\\
3 & 7
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
A =
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 2
\\
3 & 7
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)](/images/math/math-1fe0b90602bd956d6622d417fadb9a6d.png)
hacemos
![A^{-1} =
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a & b
\\
c & d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
A^{-1} =
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a & b
\\
c & d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)](/images/math/math-86eccf1851904f21df88d4e8caf4391c.png)
como
![I = A \cdot A^{-1} \Rightarrow
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 2
\\
3 & 7
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\cdot
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a & b
\\
c & d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
I = A \cdot A^{-1} \Rightarrow
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 2
\\
3 & 7
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\cdot
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a & b
\\
c & d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)](/images/math/math-83c4208e822a9057faf4bc22eb75b114.png)
Operando:
![\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a + 2c & b + 2d
\\
3a + 7c & 3b + 7d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\Leftrightarrow
\left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a + 2c & = & 1
\\
3a + 7c & = & 0
\\
b + 2d & = & 0
\\
3b + 7d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
a + 2c & b + 2d
\\
3a + 7c & 3b + 7d
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
=
\left(
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{cc}
1 & 0
\\
0 & 1
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right)
\Leftrightarrow
\left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a + 2c & = & 1
\\
3a + 7c & = & 0
\\
b + 2d & = & 0
\\
3b + 7d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.](/images/math/math-65ac35f7477a5f157f8f4b5954474b3d.png)
![\Rightarrow \left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a & = & 7
\\
b & = & -2
\\
c & = & -3
\\
d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.
\Rightarrow \left\{
</p>
<pre> \begin{array}[c]{ccc}
a & = & 7
\\
b & = & -2
\\
c & = & -3
\\
d & = & 1
\\
\end{array}
</pre>
<p>\right.](/images/math/math-d80915bcc5f5cebafc112b3692daef76.png)
Método de Gauss-Jordan
La inversa de una matriz regular
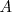 se calcular transformando la matriz
se calcular transformando la matriz
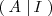 mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz
mediante operaciones elementales por filas en la matriz
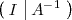
Las operaciones elementales por filas en una matriz son las siguientes:
- Intercambiar las filas
 y
y
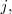 que designaremos por
que designaremos por

- Multiplicar la fila
 por el numero
por el numero
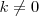 y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por
y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por
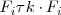
- Multiplicar la fila
 por el numero
por el numero
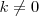 y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por
y sustituirla por el resultado; lo designamos por
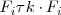
- Sumar las filas
 y
y
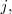 , multiplicadas por sendos números, y llevar el resultado a la fila
, multiplicadas por sendos números, y llevar el resultado a la fila
 o
o
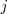 . Lo designamos por
. Lo designamos por
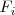 o
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]
o
[Unparseable or potentially dangerous latex formula. Error 3 ]



